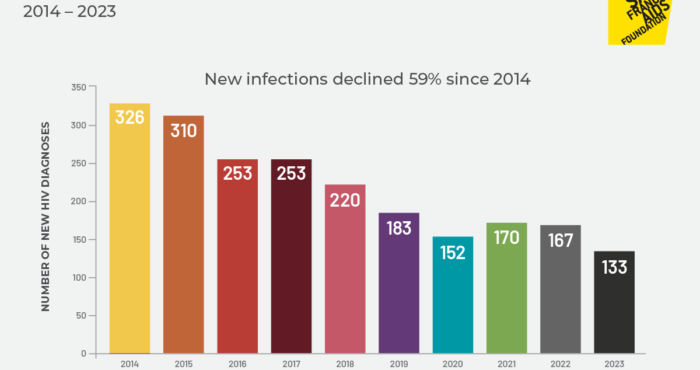
New numbers reveal the state of the HIV epidemic in the U.S.
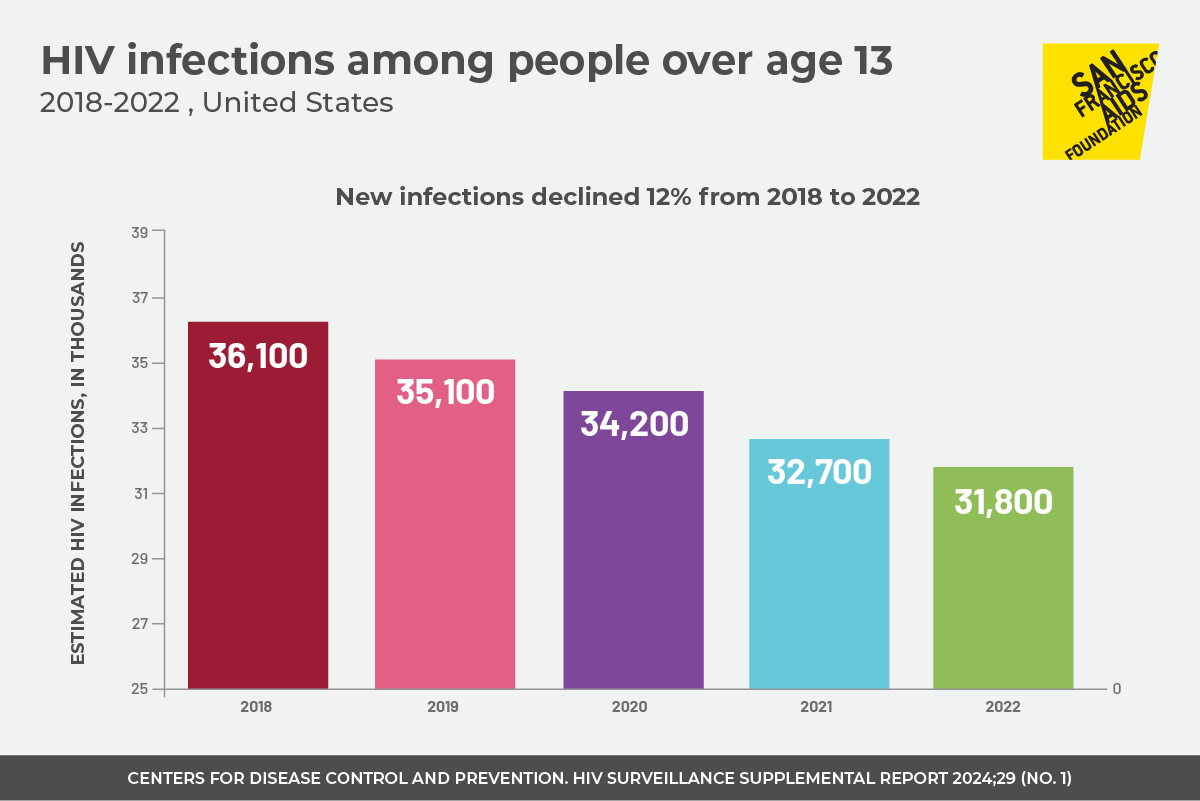
In May 2024, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released new HIV surveillance data for the U.S. through 2022. New infections across the nation decreased overall, but progress among different communities remained uneven–with some groups experiencing declines and others showing no decline or even slight increases. Here are a few notable findings from the report.
HIV prevalence
There are an estimated 1,238,000 estimated people living with HIV in the U.S. Slightly more people were aware of their status in 2022 (87%) compared to 2018 (86%).
New HIV cases
In 2022, the estimated number of HIV infections was 31,800; in 2018, the estimated number of HIV infections was 36,200. In the past four years, since 2018, HIV incidence decreased 12% among people over age 13. Increases in uptake of PrEP, HIV testing, and viral suppression likely contributed to the decline in cases, the CDC notes.
81% of new infections were among people assigned male at birth.
Trends by race & ethnicity
New infections among Black and African American individuals have declined 18% over the past four years, but still account for the highest rates of new HIV cases. 37% of all HIV infections were among Black and African American residents.
Black and African American women are disproportionately affected: In 2022, Black and African American women accounted for 47% of new HIV infections among all women.
There was no change in the rate of HIV infections among Latine community members, with 33% of all new infections happening among people who identify as Hispanic/Latino.
Trends related to substance use
Injection drug use continues to be a significant driver of the HIV epidemic. In 2022, injection drug use accounted for about 1 in 14 HIV diagnoses in the United States. About 10% of all people living with HIV are people who inject drugs.
It’s estimated that 9% of people who inject drugs and are living with HIV are unaware of their HIV status.
HIV diagnoses by age group
In the past four years, HIV incidence among younger people (age 13 – 24) has declined by 30%, while remaining steady or only slightly declining in other age groups.
HIV care
Linkage to HIV care remained high, with 82% of people newly diagnosed with HIV linked to care within one month of diagnosis. Among all people living with HIV, 65% were virally suppressed at their most recent viral load test.
For more info, read the full report from the CDC.